|
Diagnosing Communication Problems |
Previous Top Next |
Application Failures or Service Startup Failures
If an EasyHL7 service fails to start try the following:
| 1. | Open the appropriate configuration program for the affected service and verify that all of the settings are valid. If not, correct them and try restarting the service. |
| 2. | Check the .LOG file created by the service. It will be in the application folder where the service programs were installed. If it's not a "catastrophic" error there should be some cluse to be gleaned from the contents of this file. When in doubt, delete the .LOG file completely and try and restart the service, the .LOG file will be rebuilt automatically. |
| 3. | Verify that all communications pathways are 'open' and not being blocked by hardware or software firewalls. |
| 4. | Verify that the service programs themselves are not being "blocked" by DEP (see below) or the windows firewall settings. |
Windows DEP (Data Execution Prevention) can block programs that try to do 'non-standard' network communications, and sending and receiving HL7 messages over TCP/IP is certainly something that's not 'Normal' on most computers in the world. The problem actually lies in the fact that we are using the same types of communications which are continually being exploited by "hackers" to do malicious things to computer networks. So you may find it necessary to "Enable" the applications in DEP if you're computer/server is running MS WIndows XP SP2 or MS Windows Server 2003 or greater.
To get to the DEP settings:
| • | Right-click on 'My Computer' in windows explorer and select 'Properties' from the pop-up menu |
| • | Click the 'Advanced' Tab |
| • | In the 'Performance' section click the 'Settings' button |
| • | In the 'Performance Options' window click the 'Data Execution Prevention' tab. |
| • | Make the necessary changes. This usually consists of "Adding" the EasyHL7 service programs (HT_HL7Listener.exe, HT_HL7Router.exe, HT_MultiRouter.exe) and any applicable support programs like the configuration programs (ListenerConfig.exe and HT_MultiRouter_Config.exe) the EasyHL7 Services Monitor (HT_HL7Monitor.exe) and the router simulator (HT_Simulator.exe) as "exceptions" or turning DEP off altogether. |
If the EasyHL7 TCP/IP Services Monitor application won't connect to a service try the following:
| 1. | Verify that the monitor profile settings are correct. |
| 2. | Verify that the service you are trying to monitor is running. |
| 3. | Verify that all communications ports and settings are 'open' (between the computer running the monitor application and the computer running the service to be monitored) and are not being blocked by hardware or software firewalls. |
Communication between Networks
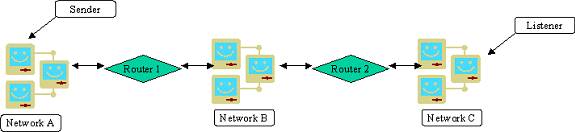
Consider the following common scenario:
A sending application on network A wishes to send HL7 messages to a computer running a listener service on network C but all connection attempts are failing and you have to diagnose exactly where the problem is occurring. You can't just move the sender closer to the listener but you can use the HL7 simulator to diagnose this problem.

Using the configuration above you would work from right to left by installing the simulator software on computers further and further from the listener and running a short simulation. When the failure occurs, you can determine where the problem is.
| 1. | Open the simulator on the Listener computer itself on Network C, and run a short simulation to verify that the listener service is configured properly and can receive messages. If it fails, the problem is on the listener computer itself or in the configuration and set up of the listener service. If it works, continue. |
| 2. | Install the simulator on another computer in Network C and run it again. If it fails, the problem is in the internal structure of Network C. If it works, continue. |
| 3. | Install the simulator on a computer in Network B and run it again. If it fails, the problem is probably in the configuration of Router 2. If it works, continue. |
| 4. | Install the simulator on a computer other than the sender on Network A and run it again. If it fails, the problem is probably in the configuration of Router 1. If it works, continue. |
| 5. | Install the simulator on the sending computer itself in Network A and run it again. If it fails, the problem is likely in the network setup/permissions of the sending computer. If it works, then the problem is somewhere in the setup and configuration of the sending application itself. |
*Helpful Hint* Settings saved in the HL7 simulator are stored in a file called HTHL7.ini in the folder where the simulator is installed. Copy this file and take it with you as you move from computer to computer and copy it into the simulator's installation folder. This could save you even more time.
So, in a maximum of 5 short steps (given the configuration above), you can determine exactly where on the network the problem is occurring which makes it that much easier for your network engineers to find and fix the problem.
See Also: VPNs and Multiple IP Addresses